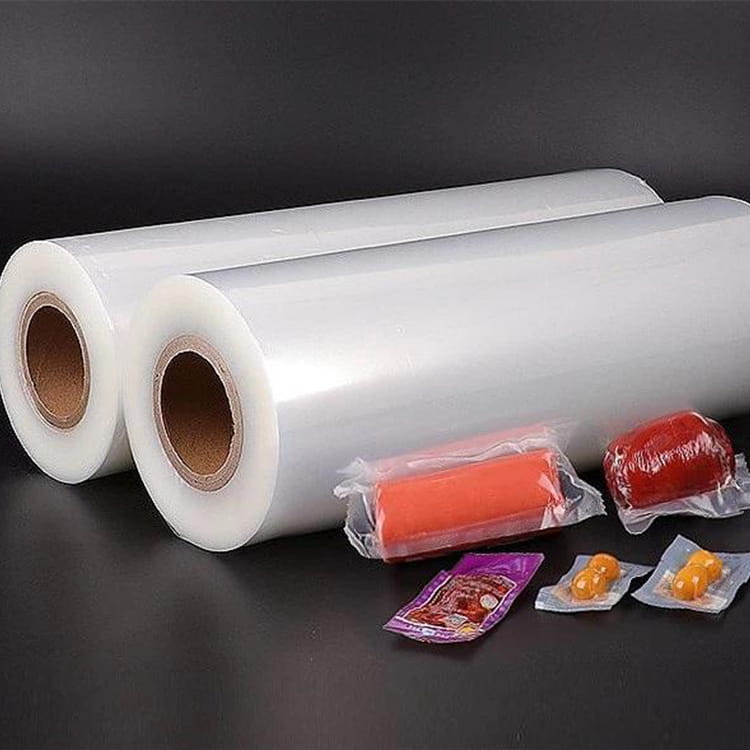
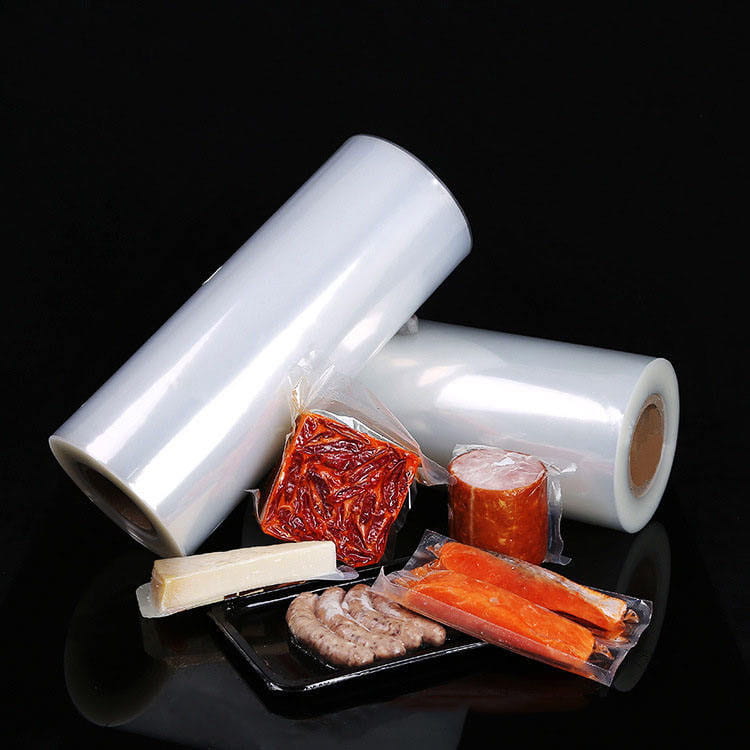
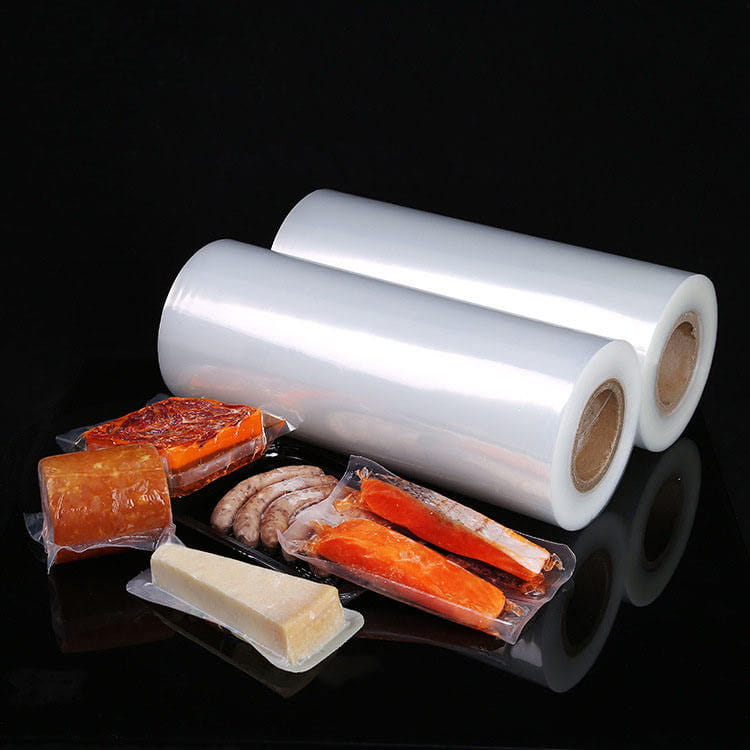
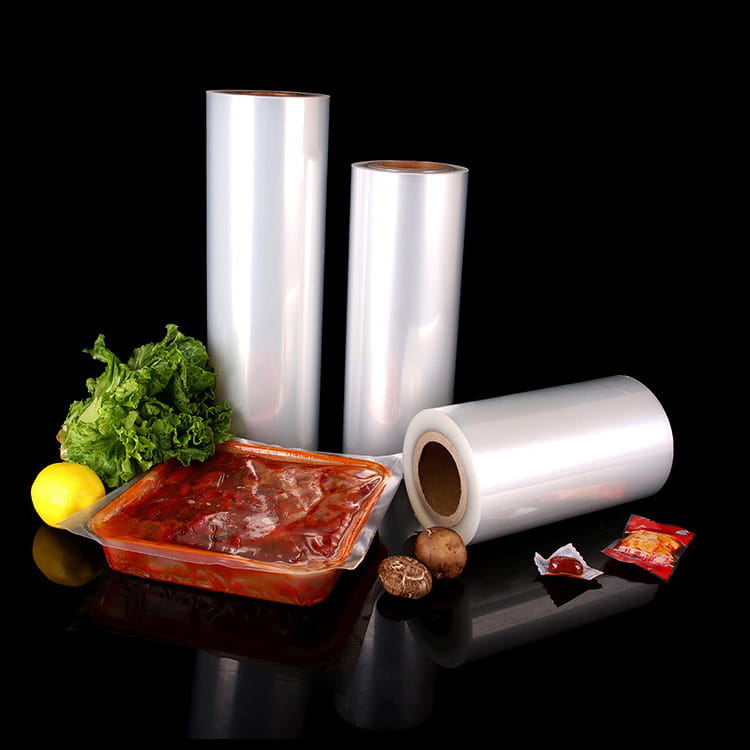
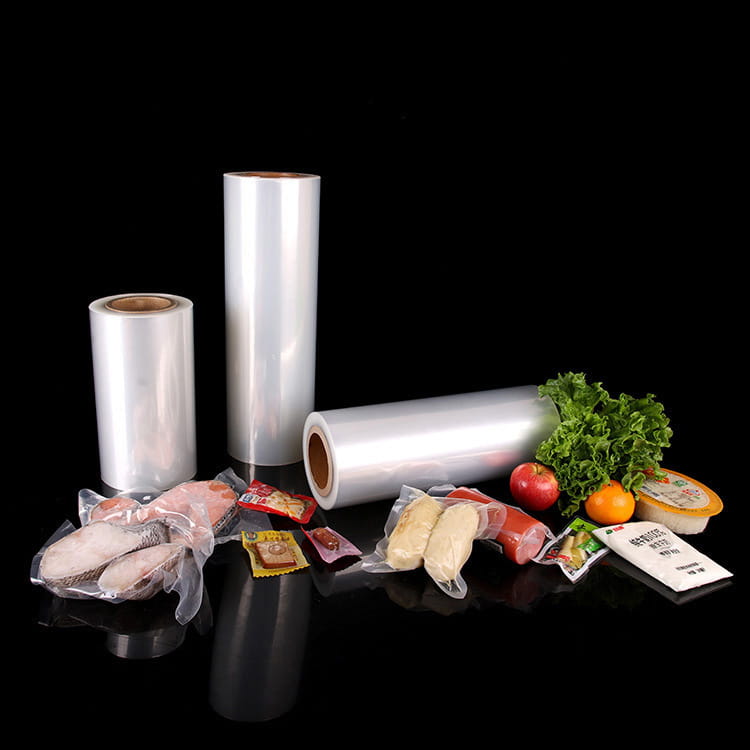
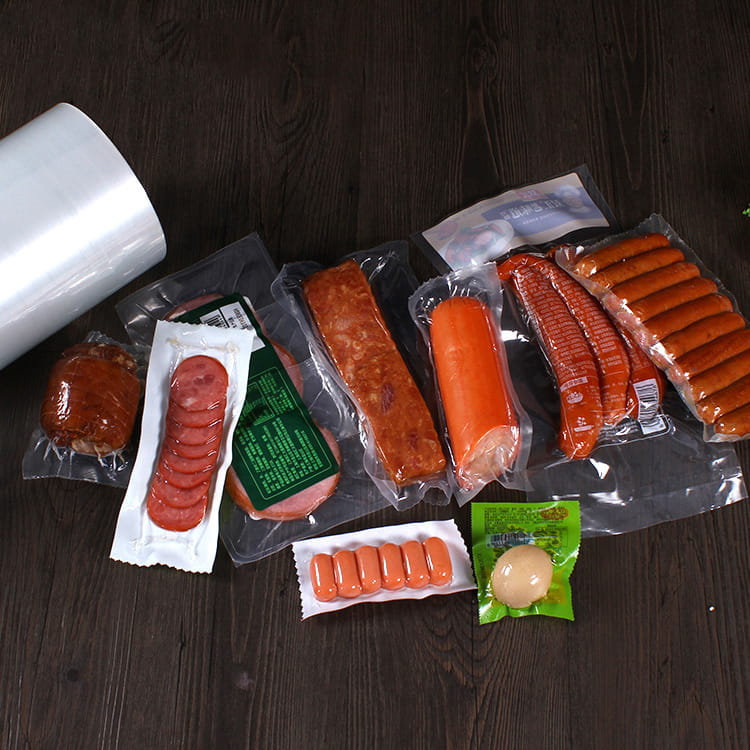
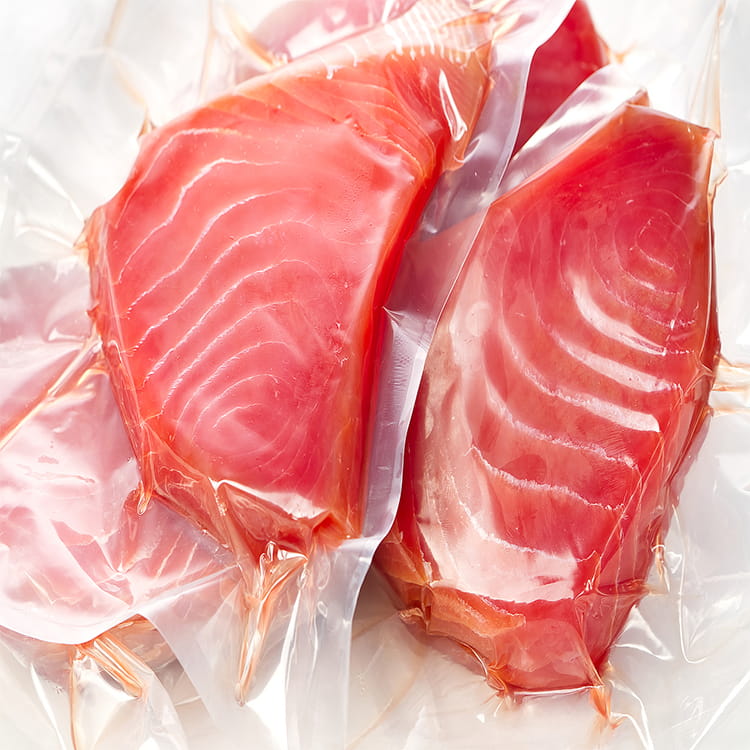
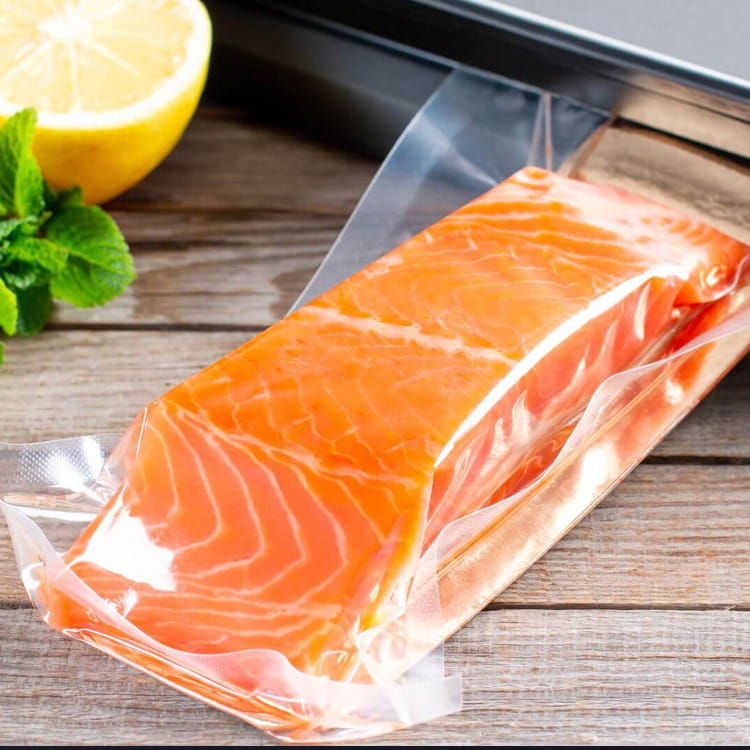
PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film has become a key material in food packaging due to its ability to preserve the integrity and quality of products. Among its many advantages, resistance to oil and fat migration is particularly important for semi-liquid, jelly, and high-fat content foods. Oil and fat migration can cause packaging degradation, compromise product appearance, and affect food safety.
Material Composition and Barrier Mechanisms
Polyamide Layer and Its Properties
The core of PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film is typically a polyamide (PA) layer, which provides mechanical strength and resistance to punctures. This layer also plays a vital role in resisting oil and fat migration. Polyamide has a dense molecular structure that minimizes the passage of non-polar substances such as oils and fats. This intrinsic property ensures that fatty liquids remain contained, maintaining product integrity.
Additionally, the PA layer contributes to oxygen and moisture barrier properties, indirectly supporting the resistance against fat migration by limiting chemical reactions that may degrade oils during storage.
Multi-layer Co-extrusion Design
Most high-performance PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film products utilize a multilayer co-extrusion design, typically combining polyamide with other polymers such as polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP). Each layer has a specific function:
- The PA layer provides strength and puncture resistance.
- The PE or PP layers contribute to heat-sealability and flexibility.
- Additional functional coatings may enhance grease resistance and barrier performance.
This multilayer configuration ensures that oil and fat molecules encounter multiple resistance points, reducing the likelihood of migration through the film.
Use of Barrier Coatings
In addition to the multilayer structure, barrier coatings are often applied to further inhibit oil and fat penetration. These coatings may include ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) or similar high-barrier polymers. Although not reactive chemically with the product, these coatings create a physical barrier, increasing the resistance of the film to fatty substances.
Mechanisms of Oil and Fat Migration Resistance
Molecular Interaction
Oil and fat molecules are generally non-polar, while polyamide is a polar polymer. This polarity difference creates low compatibility between the molecules of the film and the oils, reducing diffusion rates. By combining polyamide with non-polar sealing layers, PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film can block migration without altering the food product.
Structural Integrity
The mechanical integrity of the film is critical in resisting oil and fat migration. Any pinholes, microcracks, or uneven surfaces can create pathways for fat molecules. Advanced PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film undergoes stringent quality control during production to maintain uniform thickness and smooth surfaces, ensuring consistent barrier performance.
Heat-Sealing Quality
Proper sealing is essential in preventing migration. The heat-sealable layer of PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film forms a strong bond with the container or tray, eliminating gaps that could allow oil seepage. Controlled sealing temperature, pressure, and dwell time are critical factors to optimize this barrier.
Factors Affecting Oil and Fat Resistance
Film Thickness
Thicker films generally provide better resistance, as oil and fat molecules must traverse a greater distance to migrate. However, increasing thickness also affects flexibility and cost. Manufacturers balance these factors to meet the requirements of jelly and high-fat food packaging.
Storage Conditions
Temperature fluctuations can affect the film’s resistance to oils and fats. High temperatures may increase polymer mobility, slightly enhancing migration rates. PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film is designed to withstand typical refrigeration, ambient storage, and moderate heating conditions, maintaining barrier performance.
Product Characteristics
The type of fat or oil and its concentration influence migration potential. Semi-solid or viscous jellies with dispersed fats may exert localized pressure on the film. The multilayer structure and PA layer density provide localized reinforcement to resist this pressure.
Industry Applications
Food Packaging
PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film is extensively used in ready-to-eat desserts, jelly cups, and high-fat spreads. Its oil and fat resistance ensures that products retain their shape and appearance while preventing container contamination.
Meat and Dairy Products
In vacuum-packaged meats, cheese, or butter, fat migration can compromise both the package and the product’s shelf life. PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film prevents leakage while maintaining the vacuum seal.
Convenience Foods
For processed meals and pre-packaged foods with sauces, the film’s resistance to grease migration allows manufacturers to use vacuum packaging without risk of compromising product quality.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Standardized Testing
Manufacturers assess the oil and fat resistance of PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film using industry-standard methods, such as grease penetration tests and visual inspections after storage under controlled conditions.
| Test Type | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Grease penetration test | Measure film permeability to oils | Film is exposed to fatty substances and inspected for penetration |
| Puncture resistance | Assess integrity under pressure | Ensures oil cannot migrate through micro-damage |
| Thermal sealing evaluation | Verify seal quality | Tests if heat-sealed joints remain intact under stress |
Batch Control
Consistent performance requires rigorous batch testing, including thickness uniformity, surface smoothness, and barrier property verification. Buyers and manufacturers often request technical data sheets documenting these properties.
Advantages for Buyers and Manufacturers
- Reduced product contamination: Oils and fats remain contained, improving shelf life.
- Enhanced packaging reliability: Strong seals reduce leakage risk.
- Improved consumer perception: Clear, intact packaging improves product appeal.
- Compatibility with automated lines: The film’s strength and flexibility make it suitable for high-speed vacuum packaging equipment.
Sustainability Considerations
While PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film provides excellent barrier performance, sustainability is increasingly important. Manufacturers optimize film formulations to minimize material usage while maintaining oil and fat resistance. Some films incorporate recyclable components or thinner multilayer designs to reduce environmental impact without sacrificing performance.
Conclusion
PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film resists oil and fat migration through a combination of material properties, multilayer structure, barrier coatings, and sealing quality. Its dense polyamide core, coupled with heat-sealable layers, ensures that semi-liquid and high-fat products remain contained, maintaining both product integrity and consumer safety.
For food producers, understanding the technical and practical aspects of this film allows for more effective packaging solutions, optimized shelf life, and better product presentation. Proper selection and handling of PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film are crucial in applications ranging from desserts and jellies to meats and processed meals.
By adhering to production standards, optimizing storage conditions, and choosing films with proven barrier performance, manufacturers and buyers can reliably use PA Plastic Jelly Sealing Vacuum Packaging Film to protect products from oil and fat migration while meeting industry requirements.


 English
English عربى
عربى