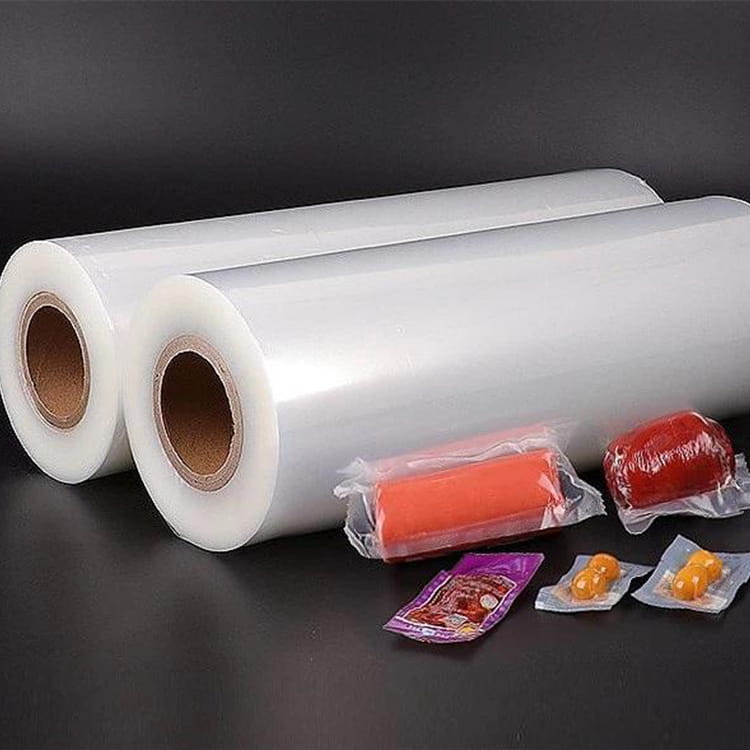
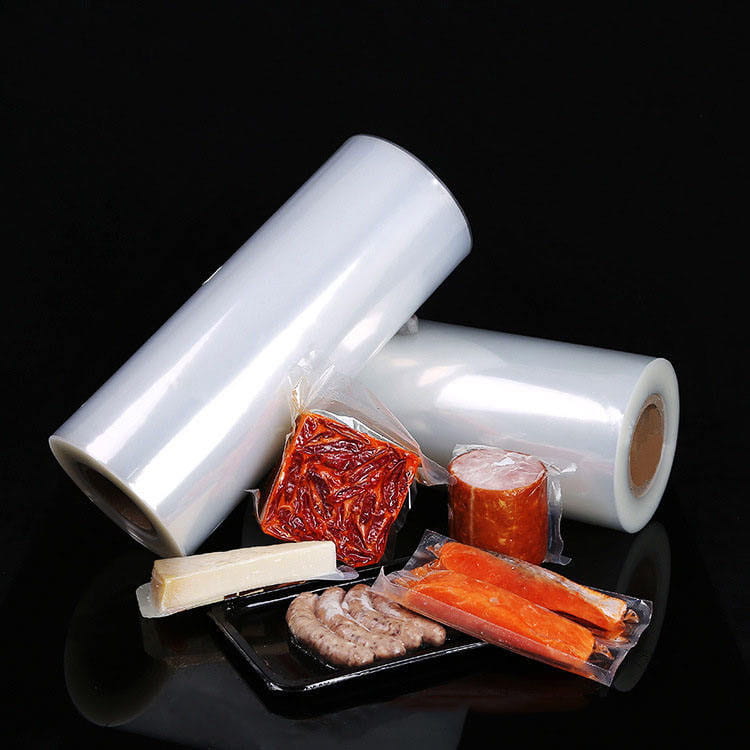
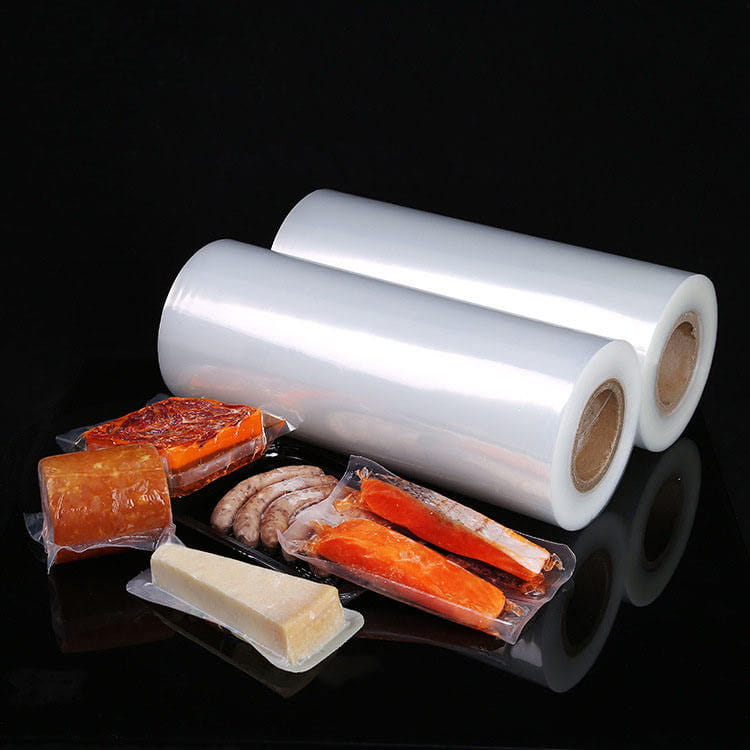
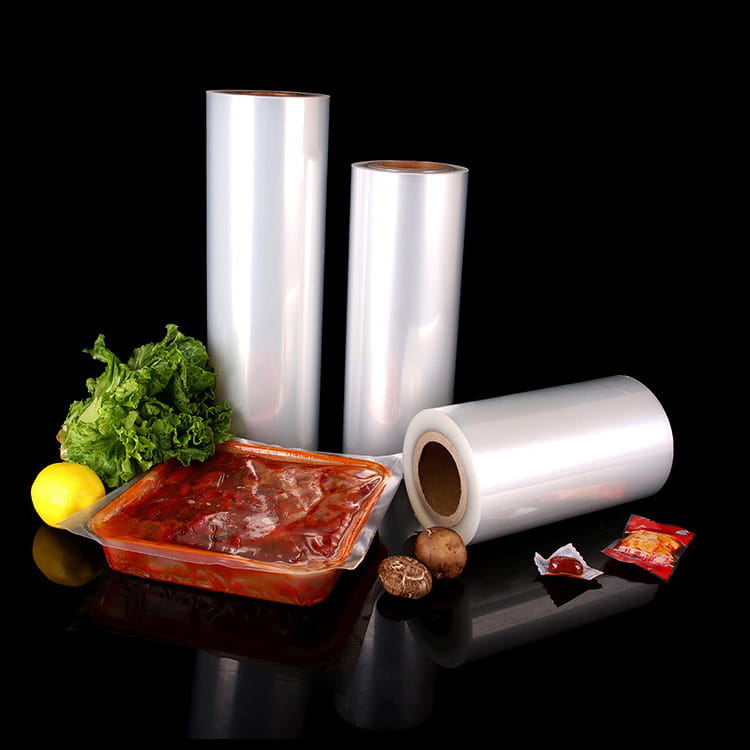
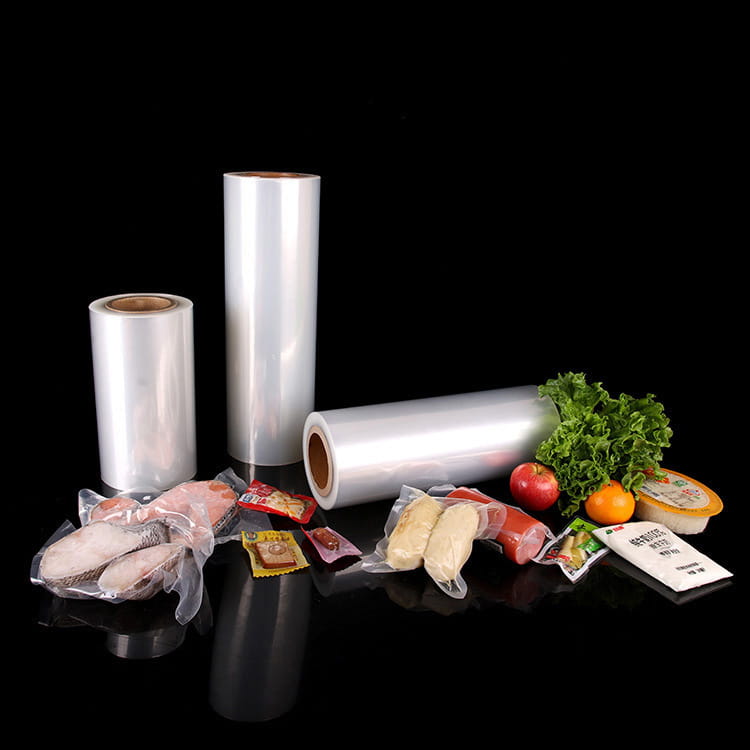
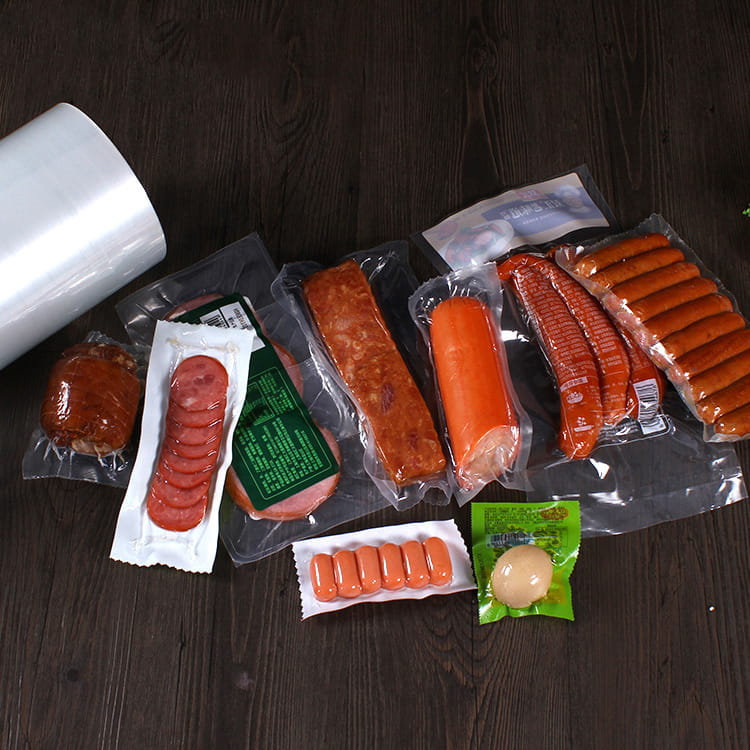
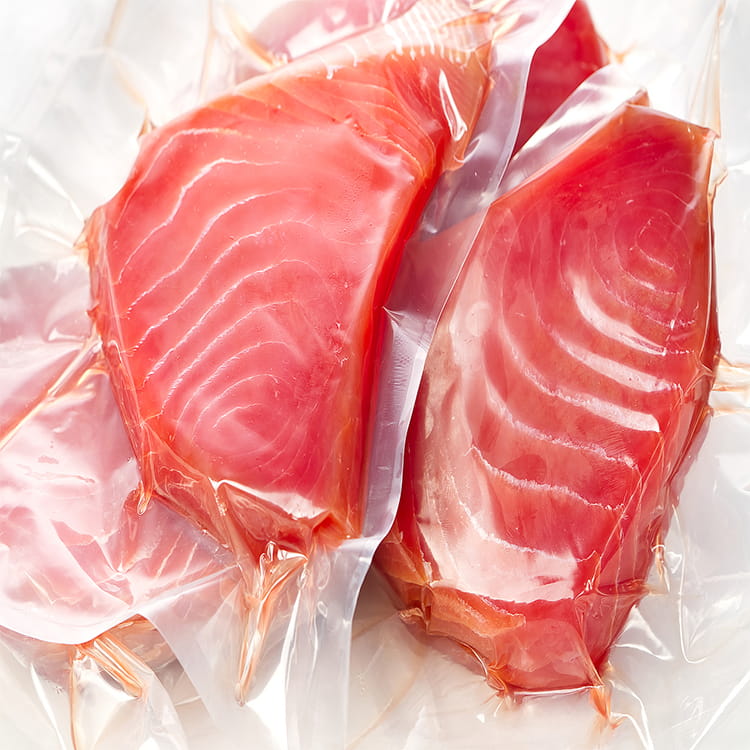
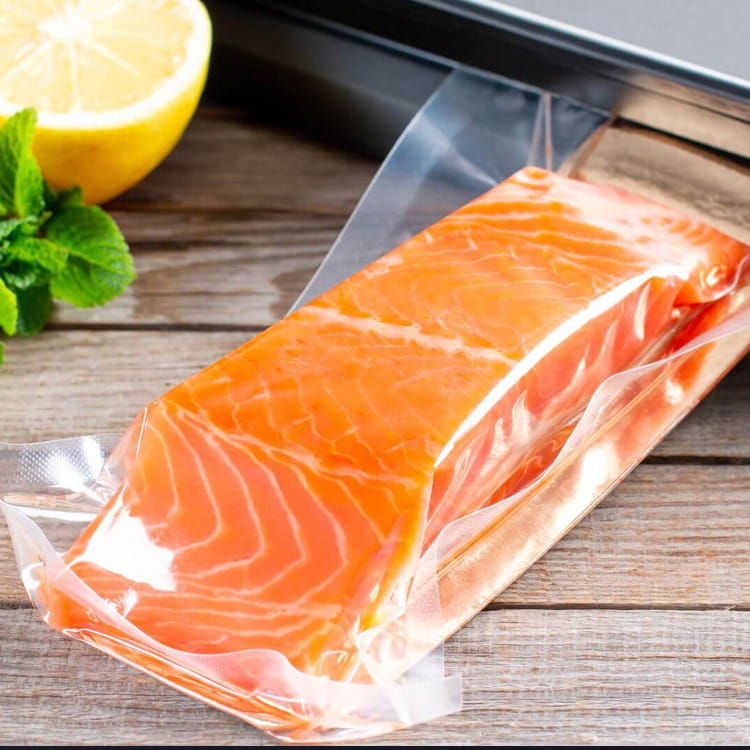
Food grade 5-layer coextruded top and bottom high barrier film has become a critical material in modern food packaging due to its combination of barrier performance, mechanical strength, and visual appeal. Among its many attributes, transparency plays a crucial role in both consumer perception and product presentation. Maintaining high clarity is essential for products such as snacks, confectionery, frozen foods, and ready-to-eat meals, where the visibility of the contents can directly influence purchase decisions.
Transparency in coextruded films is not simply a result of the raw materials used; it is the outcome of a carefully engineered interplay between polymer selection, layer configuration, extrusion process, and post-processing conditions.
Material Composition and Layer Structure
The clarity of food grade 5-layer coextruded top and bottom high barrier film is largely determined by the choice of polymers and the configuration of the five layers. Typically, the film consists of:
- Top layer – Provides printability, surface smoothness, and chemical resistance. Transparent polymers such as PET or high-grade PE are commonly used.
- Tie layers – Serve to bond incompatible materials within the film structure. They are usually based on modified polyolefins to ensure adhesion without affecting optical properties.
- Barrier layer – Often composed of EVOH (ethylene vinyl alcohol) or similar high-barrier polymers. This layer provides oxygen and moisture resistance. Maintaining its transparency requires careful control of polymer crystallinity and thickness.
- Bottom layer – Provides heat-sealability and mechanical support. Transparent PE or PP is commonly used to preserve clarity.
Table 1: Typical Layer Composition of Food Grade 5-Layer Coextruded Top and Bottom High Barrier Film
| Layer | Material | Primary Function | Contribution to Transparency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top Layer | PET / PE | Printability & chemical resistance | Provides smooth surface for visual clarity |
| Tie Layer 1 | Modified PE | Adhesion | Minimal impact on optical properties |
| Barrier Layer | EVOH | Oxygen & moisture barrier | Requires low crystallinity to maintain clarity |
| Tie Layer 2 | Modified PE | Adhesion | Minimal impact on optical properties |
| Bottom Layer | PE / PP | Heat sealing & mechanical support | Maintains transparency and flexibility |
Polymer Selection and Optical Clarity
Transparency in multi-layer films is influenced by the refractive index compatibility between layers. When the refractive indices of adjacent layers closely match, light passes through with minimal scattering, preserving clarity. In food grade 5-layer coextruded top and bottom high barrier film, manufacturers carefully select polymers and additives to minimize haze. Common strategies include:
- Using high-purity resins with low levels of fillers and pigments.
- Controlling crystallinity during extrusion to avoid light-scattering regions.
- Incorporating anti-blocking agents in minute amounts to prevent surface sticking without creating visible white specks.
The barrier layer, usually EVOH, is inherently more crystalline than PE or PP. To maintain transparency, its thickness is optimized, and processing temperatures are precisely controlled to minimize crystal formation, which can cause cloudiness.
Coextrusion Process and Layer Integration
The coextrusion process is central to achieving uniform optical properties. Key factors include:
- Die design and flow control – Ensures that each layer is of uniform thickness and free from streaks or thickness variations.
- Temperature management – Precise thermal control during extrusion prevents premature crystallization of polymers, particularly the barrier layer.
- Layer interface compatibility – Tie layers prevent delamination while maintaining optical clarity by minimizing refractive index mismatch.
Advanced extrusion lines use computer-controlled thickness monitoring to ensure consistent layer distribution. Any deviation can cause haziness, streaks, or opacity.
Surface Properties and Finish
The surface finish of both the top and bottom layers significantly affects transparency. Smooth surfaces reduce diffuse reflection and maintain a glossy, clear appearance. Techniques to enhance surface properties include:
- Polishing or chill roll control during extrusion.
- Minimizing surface roughness to below 0.5 microns, which prevents light scattering.
- Selecting materials with high intrinsic gloss.
Additives and Their Role in Clarity
While additives are often required for processing or barrier performance, they must be carefully controlled. Common additives in food grade 5-layer coextruded top and bottom high barrier film include:
- Slip agents – Facilitate processing without reducing clarity.
- Anti-block agents – Used sparingly to prevent film layers from sticking.
- UV stabilizers – Protect the film from degradation but can sometimes affect transparency if overused.
Table 2: Additives in Food Grade 5-Layer Coextruded Top and Bottom High Barrier Film and Their Effects
| Additive | Purpose | Effect on Transparency |
|---|---|---|
| Slip agent | Reduce friction during processing | Minimal if properly dispersed |
| Anti-block | Prevent layer adhesion | Can slightly reduce clarity if overused |
| UV stabilizer | Prevent degradation from light | Requires careful selection to avoid haze |
| Clarifiers | Enhance optical properties | Improves transparency by reducing crystallinity |
Post-Processing Considerations
Even after coextrusion, transparency can be affected by post-processing operations such as:
- Thermoforming – Stretching the film can align polymer chains and improve clarity, but excessive deformation may induce haziness.
- Printing and coating – Printing should avoid excessive ink penetration into the film layers. Surface coatings may be applied to preserve gloss without affecting transparency.
- Lamination – When combined with other films, optical matching is critical to avoid reducing clarity.
Quality Control and Testing
Maintaining transparency requires rigorous quality control. Common inspection methods include:
- Haze measurement – Quantifies light scattering; low haze indicates high clarity.
- Gloss measurement – Ensures the film maintains visual appeal.
- Visual inspection – Detects streaks, bubbles, or inclusions that affect transparency.
These parameters are especially critical for films intended for consumer-packaged goods, where visibility of the product is a key marketing factor.
Applications Highlighting Transparency
The transparent nature of food grade 5-layer coextruded top and bottom high barrier film allows its use in a variety of applications, including:
- Snack packaging – Consumers can see product quality directly.
- Fresh and frozen foods – Transparency facilitates display in retail while protecting against oxygen and moisture.
- Ready-to-eat meals – Enables portion visualization without opening the package.
- Confectionery and bakery items – Maintains product appearance and attractiveness.
Transparency combined with high barrier performance ensures that products are both visible and well-protected.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Maintaining transparency in films that are also eco-friendly is a growing concern. Strategies include:
- Reducing additive load while preserving clarity.
- Using recyclable polyolefin layers where possible.
- Optimizing barrier layer thickness to reduce material usage without sacrificing optical or protective performance.
These considerations ensure that food grade 5-layer coextruded top and bottom high barrier film remains competitive in sustainable packaging markets.
Conclusion
Transparency in food grade 5-layer coextruded top and bottom high barrier film is achieved through a combination of material selection, precise layer engineering, coextrusion process control, surface finish optimization, and careful additive management. Its clear appearance enhances product visibility, consumer appeal, and marketability while maintaining critical barrier properties for food protection. Ongoing innovations continue to improve both the optical properties and environmental footprint of this versatile packaging material.
FAQ
Q1: Can food grade 5-layer coextruded top and bottom high barrier film maintain clarity under freezing conditions?
Yes, proper polymer selection and processing control allow the film to retain transparency even at low temperatures.
Q2: Does printing affect the transparency of food grade 5-layer coextruded top and bottom high barrier film?
Printing can slightly reduce clarity if excessive ink penetrates the film; surface coatings and ink management minimize this effect.
Q3: Can the film be recycled while maintaining its transparent properties?
Recycling is feasible, particularly with polyolefin-based layers, though barrier materials like EVOH may require specialized recycling processes.
Q4: How is haze measured in this film?
Haze is measured using standardized optical instruments that quantify the light scattering of the film.
Q5: Are additives like UV stabilizers and anti-block agents harmful to transparency?
When used correctly and in controlled amounts, these additives minimally impact transparency while enhancing durability and processability.
References
- Packaging Technology and Science, Volume 33, Issue 7, 2020 – Multilayer Film Structures and Optical Properties.
- Journal of Applied Polymer Science, Volume 138, Issue 12, 2021 – Barrier Polymers in Food Packaging Films.
- Food Packaging Forum, 2022 – Advances in Transparent High-Barrier Food Films.


 English
English عربى
عربى