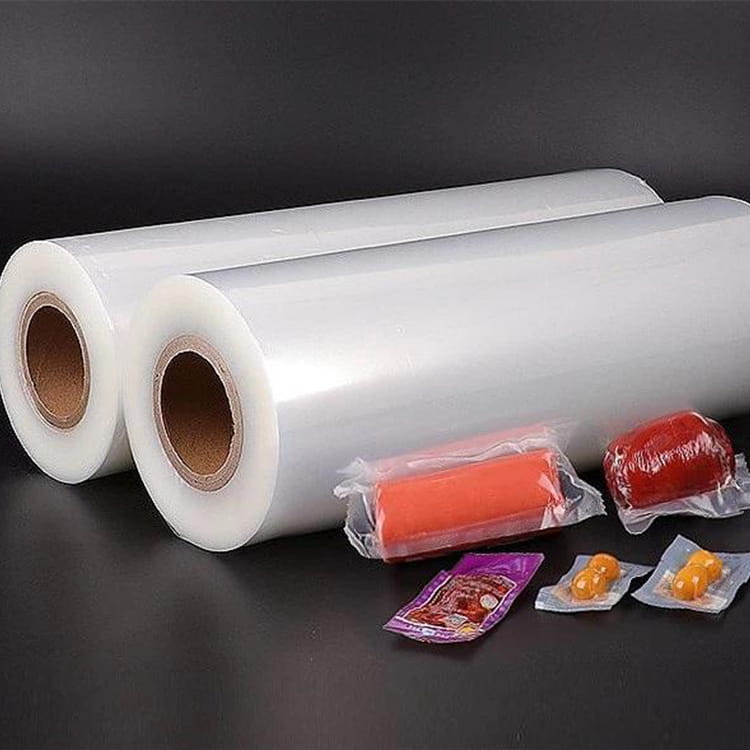
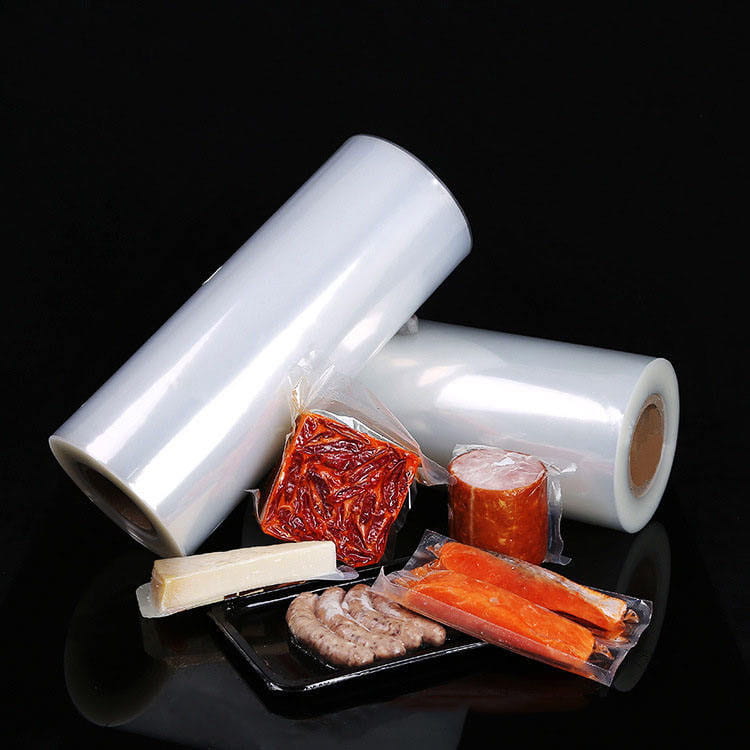
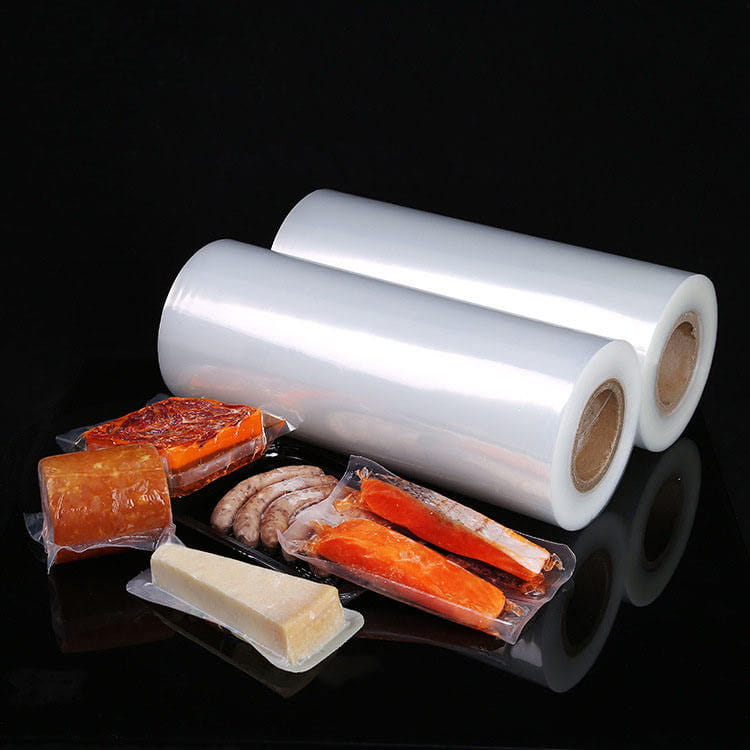
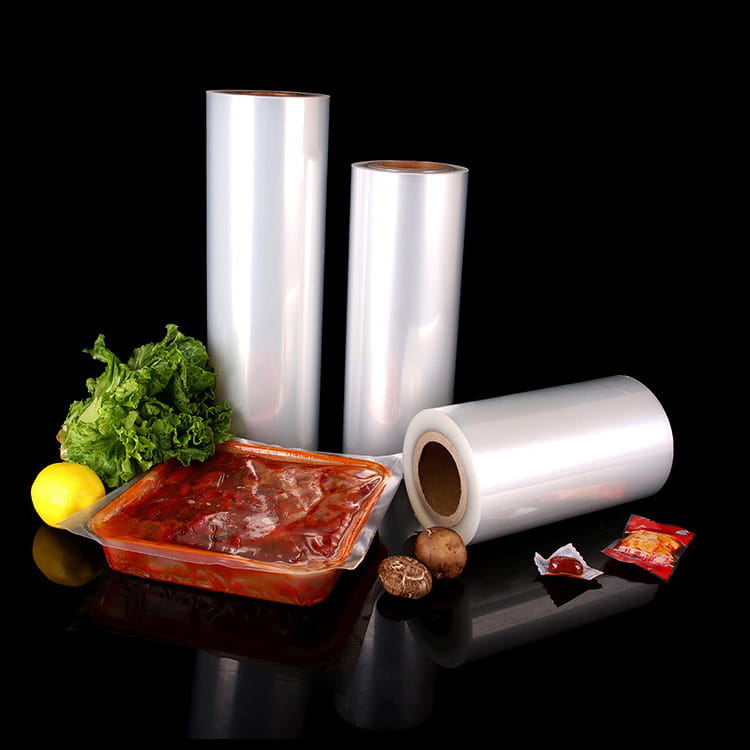
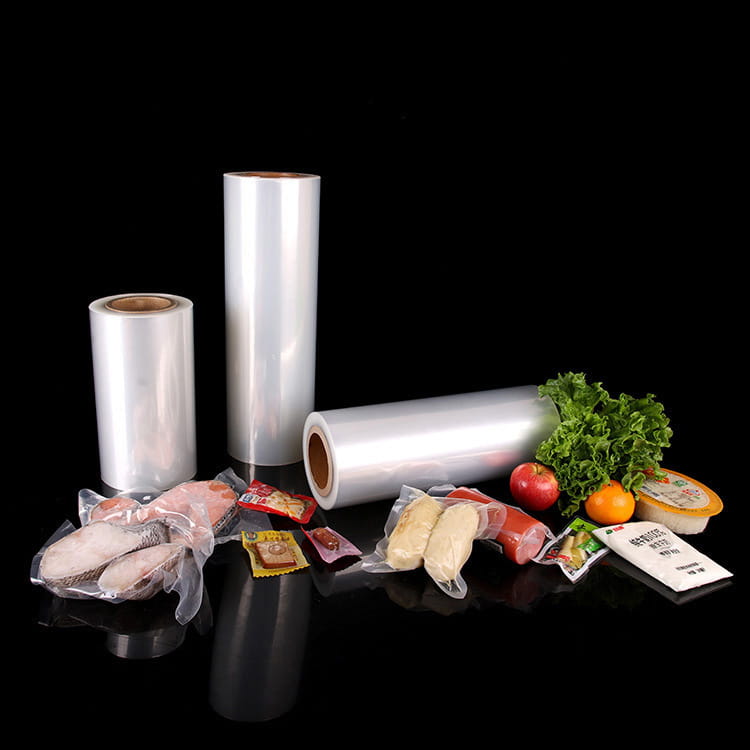
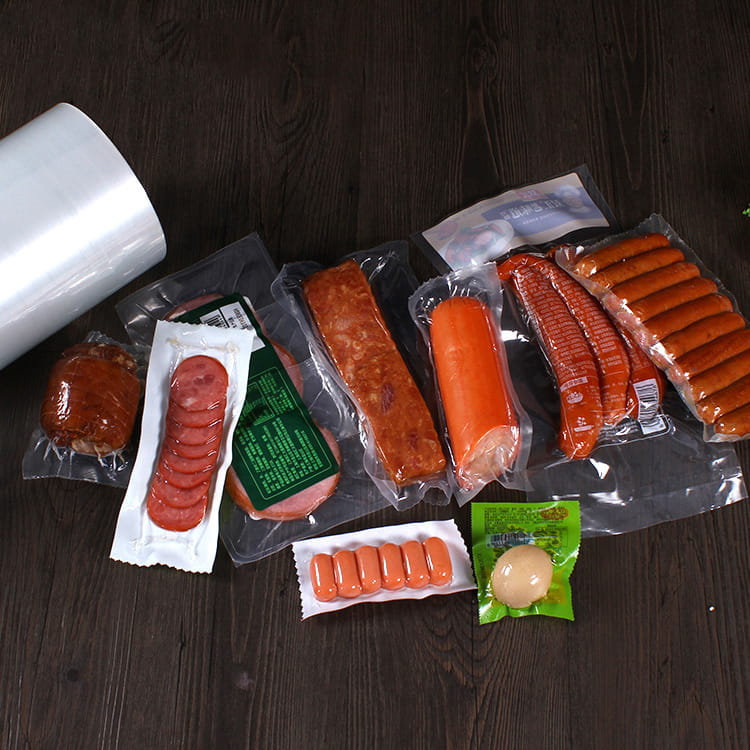
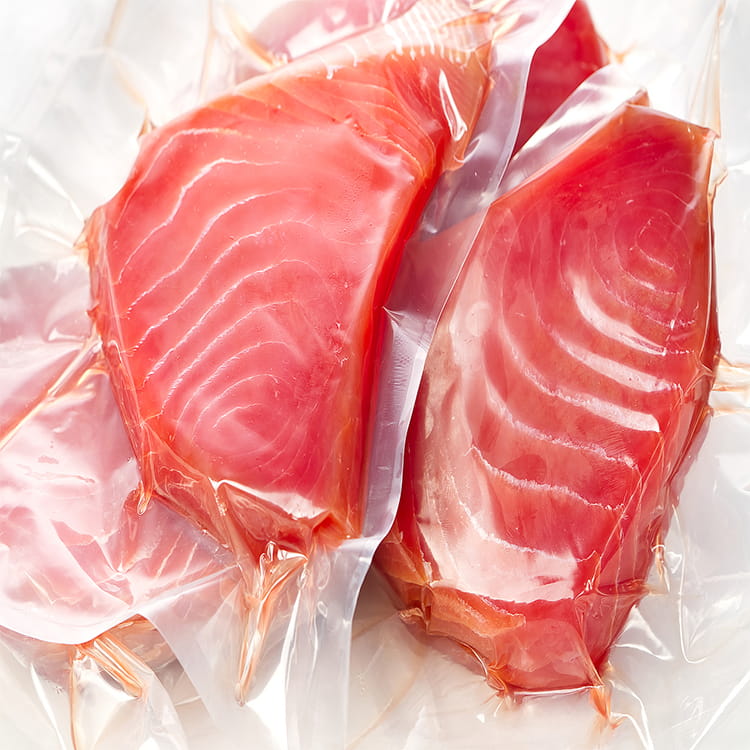
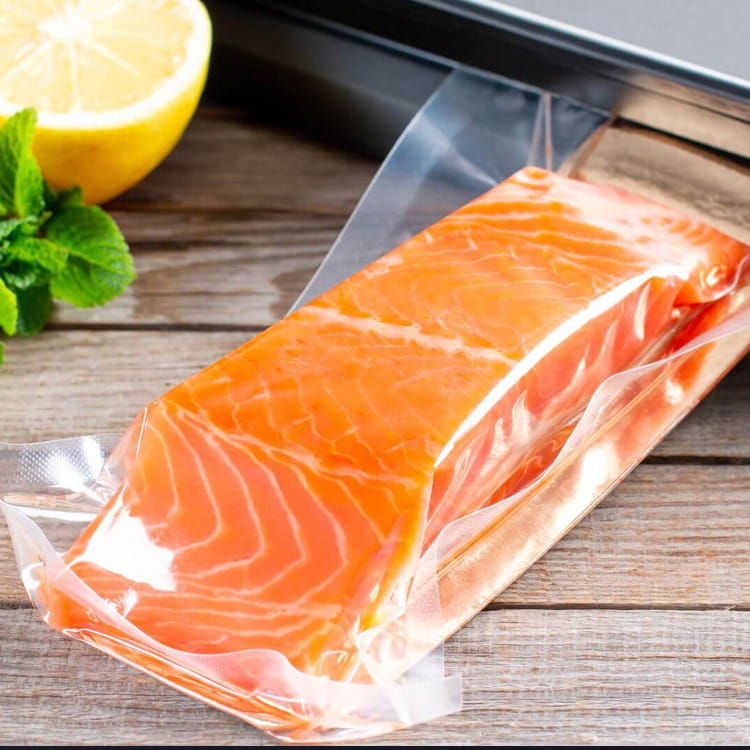
Transparent co-extruded plastic packaging film has become a significant component in modern food packaging systems. Unlike single-layer films, co-extruded films combine multiple polymer layers, each engineered to provide specific functional characteristics. This multi-layer approach addresses critical requirements such as mechanical strength, barrier properties, and aesthetic transparency, all of which are essential for food safety, shelf-life extension, and consumer appeal.
Material Composition and Engineering Principles
Transparent co-extruded plastic packaging film typically consists of layers made from polyethylene (PE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polypropylene (PP), or ethylene-vinyl alcohol (EVOH), arranged in a manner that balances strength, barrier properties, and flexibility. Each layer serves a distinct role:
- Structural Layer: Provides tensile strength, puncture resistance, and dimensional stability.
- Barrier Layer: Controls gas, moisture, and aroma permeability, crucial for perishable food products.
- Sealant Layer: Ensures reliable heat-sealing, critical for maintaining product integrity.
- Tie Layer: Enhances adhesion between layers that would otherwise be incompatible.
From a system engineering standpoint, the combination of these layers must be optimized not only for individual material performance but also for the overall interaction of layers under thermal, mechanical, and environmental stresses.
Functional Advantages in Food Packaging
1. Barrier Performance
Transparent co-extruded films offer a multi-dimensional barrier against oxygen, moisture, and volatile compounds. By incorporating materials such as EVOH in a central layer, engineers can significantly reduce oxygen transmission rates (OTR), which directly correlates with the preservation of sensitive nutrients and flavor compounds in food products.
2. Mechanical Integrity
The combination of high-strength polymers ensures that packaging films can withstand transport stresses, stacking, and consumer handling. Engineers often consider tensile strength, elongation at break, and puncture resistance during film selection to align with specific packaging requirements.
3. Process Compatibility
Transparent co-extruded films are designed to perform reliably on high-speed filling and sealing equipment. Their thermal properties, sealability, and coefficient of friction must be carefully tuned to prevent machine jams, incomplete seals, or product contamination.
4. Visual Transparency
Transparency is not merely aesthetic; it facilitates quality control, enables product visibility for consumers, and supports regulatory compliance in labeling. Engineering the optical properties of multi-layer films requires balancing clarity, haze, and gloss while maintaining mechanical and barrier performance.
Design Considerations for Food Packaging Systems
When integrating transparent co-extruded plastic packaging film into food packaging systems, engineers must evaluate multiple factors:
| Design Parameter | Engineering Considerations | Impact on Packaging System |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Composition | Material selection for each layer (PE, PET, PP, EVOH) | Balances barrier, mechanical, and sealing properties |
| Layer Thickness | Uniformity across roll width | Influences OTR, MVTR, and mechanical strength |
| Sealant Properties | Heat sealability, temperature range, seal strength | Ensures hermetic sealing, preventing contamination |
| Optical Properties | Transparency, haze, gloss | Supports consumer perception and inspection processes |
| Environmental Resistance | Temperature, humidity, UV exposure | Maintains integrity across storage and distribution |
Integration into Packaging Lines
Transparent co-extruded films must be evaluated in the context of the entire packaging line. Factors include:
- Thermal Management: Seal bars and jaws must match film thermal characteristics.
- Tension Control: Film web tension must be optimized to prevent wrinkling or tearing.
- Friction and Static Control: Surface treatments may be required to improve machine handling.
- Compatibility with Filling Medium: Films must resist chemical interactions with food, sauces, or oils.
Sustainability and Regulatory Considerations
Modern food packaging systems increasingly prioritize sustainability. Engineers are exploring transparent co-extruded films that reduce material use while maintaining performance. Multi-layer films enable thin-gauge designs without compromising barrier or mechanical integrity. Moreover, regulatory compliance, including FDA or EU food contact standards, is essential. Each polymer layer must be assessed for migration limits, safety under heat exposure, and chemical inertness.
System-Level Impact and Optimization
A system-level view considers how transparent co-extruded plastic packaging films interact with logistics, storage, and consumer use:
- Shelf-Life Extension: Reduced oxygen and moisture ingress directly correlates with extended shelf life.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Lightweight, high-strength films reduce transportation costs.
- Waste Reduction: Improved barrier and mechanical performance minimizes product spoilage.
- Consumer Experience: Visual clarity and structural integrity enhance perception and usability.
Table: Comparative Performance Metrics for Multi-Layer Films (Illustrative)
| Film Property | Single-Layer Film | Transparent Co-Extruded Film | System-Level Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Barrier | Moderate | High (with EVOH layer) | Extended shelf life, preserved flavor |
| Moisture Barrier | Limited | High (with PE/PP layers) | Reduced product dehydration |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate | High | Handles transport and packaging stresses |
| Heat Seal Reliability | Variable | Consistent | Ensures hermetic packaging |
| Transparency | High | High | Supports product visibility and QC |
Conclusion
Transparent co-extruded plastic packaging film is a critical enabler in modern food packaging systems. Its multi-layer construction addresses mechanical, barrier, sealing, and optical requirements simultaneously. From a systems engineering perspective, selecting, designing, and integrating these films requires careful consideration of material properties, manufacturing processes, regulatory compliance, and system-level performance metrics. By approaching food packaging through a holistic lens, engineers and technical managers can optimize packaging solutions that maintain food quality, support operational efficiency, and meet consumer expectations.
FAQ
Q1: Can transparent co-extruded films be recycled?
A1: Multi-layer films are more challenging to recycle than mono-material films. However, advances in material separation and chemical recycling are improving end-of-life options.
Q2: How do engineers optimize barrier properties in co-extruded films?
A2: Barrier optimization involves selecting appropriate materials (e.g., EVOH), adjusting layer thicknesses, and ensuring uniform co-extrusion to minimize defects.
Q3: Are transparent co-extruded films suitable for all types of food products?
A3: These films are versatile but must be matched to the specific requirements of food type, shelf life, and processing conditions.
Q4: What are the primary challenges in integrating co-extruded films into packaging lines?
A4: Challenges include matching thermal sealing parameters, tension control, friction management, and chemical compatibility with food.
Q5: How does transparency affect packaging system performance?
A5: Transparency facilitates inspection, improves consumer perception, and enables regulatory compliance, all while requiring careful engineering to maintain mechanical and barrier properties.
References
- Robertson, G. L. (2021). Food Packaging: Principles and Practice. CRC Press.
- Marsh, K., & Bugusu, B. (2007). Food Packaging—Roles, Materials, and Environmental Issues. Journal of Food Science, 72(3), R39–R55.
- Yam, K. L. (2019). Encyclopedia of Packaging Technology. Springer.


 English
English عربى
عربى