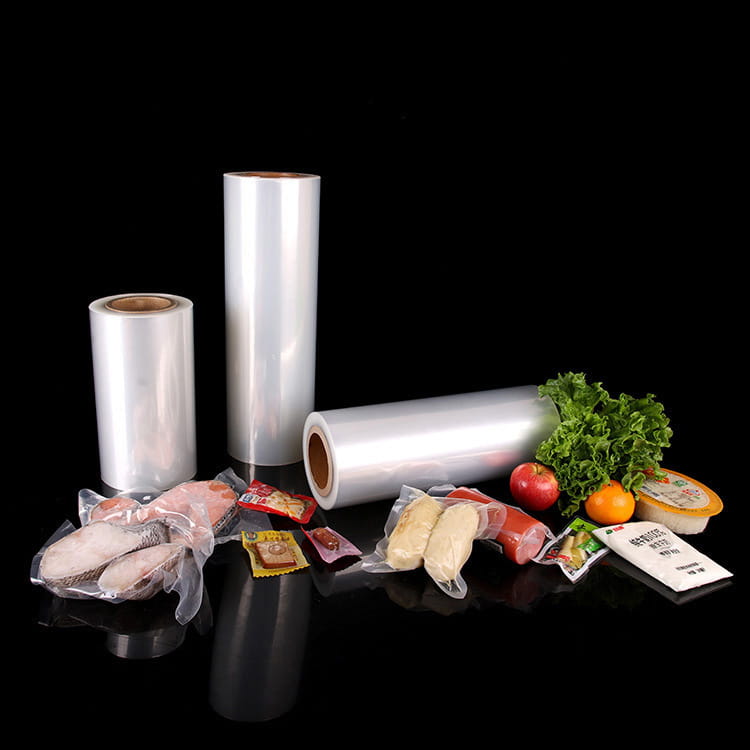
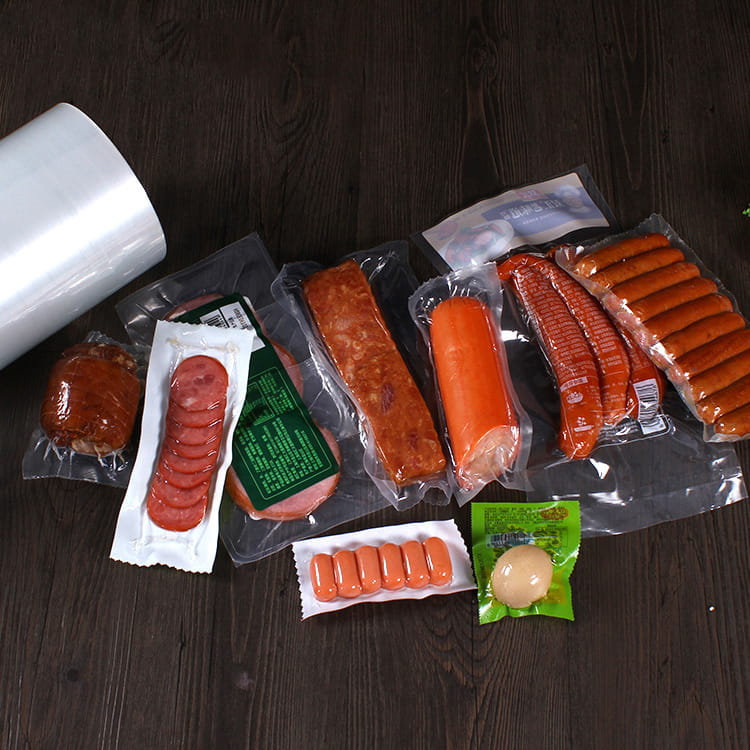
multi-layer co-extruded barrier film has become an essential material in modern packaging due to its ability to protect products from environmental factors, extend shelf life, and maintain product integrity. One of the most critical properties of this film is its moisture barrier performance, which directly impacts the quality and durability of packaged goods.
Understanding multi-layer co-extruded barrier film
Multi-layer co-extruded barrier film is produced by combining multiple polymer layers through a co-extrusion process. Each layer is designed to provide specific characteristics, such as mechanical strength, barrier protection, or sealability. The combination of layers allows manufacturers to tailor the film to meet the precise requirements of different applications, including food packaging, pharmaceuticals, and industrial uses.
A typical multi-layer co-extruded barrier film structure includes:
| Layer Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Core barrier layer | Provides primary resistance against moisture, oxygen, and other gases |
| Tie layer | Ensures adhesion between incompatible polymers |
| Outer layer | Provides mechanical strength and printability |
| Inner seal layer | Facilitates heat sealing and product containment |
The performance of the film, particularly its moisture barrier properties, depends on the selection of materials for each layer, their thickness, and the uniformity of the co-extrusion process.
Materials influencing moisture barrier performance
Improving moisture barrier performance begins with careful selection of materials. Different polymers exhibit varying levels of water vapor transmission resistance.
- Polyethylene (PE): Widely used for its sealability and mechanical strength, though it has moderate moisture barrier properties on its own.
- Polyamide (PA or Nylon): Offers strong mechanical performance and excellent barrier against gases but moderate moisture resistance.
- Ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH): Highly effective in preventing oxygen and moisture penetration, often used as the core barrier layer in multi-layer constructions.
- Polypropylene (PP): Provides heat resistance and rigidity but requires complementary layers to enhance moisture protection.
By strategically combining these polymers, multi-layer co-extruded barrier film can achieve a balance of moisture barrier performance, flexibility, and durability.
Layer optimization strategies
Increasing core barrier thickness
The core barrier layer plays the most significant role in preventing moisture transmission. Increasing its thickness enhances the film’s resistance to water vapor. However, excessive thickness can increase cost and reduce flexibility, so a balance must be achieved. Manufacturers often optimize the thickness of moisture-resistant polymers, such as EVOH, to maximize barrier performance without compromising other film properties.
Using multi-barrier approaches
Some multi-layer co-extruded barrier films incorporate multiple thin barrier layers separated by tie layers. This multi-barrier configuration creates a more tortuous path for moisture, significantly improving the film’s overall resistance. The technique is particularly useful in packaging sensitive food products where maintaining low water activity is critical.
Optimizing tie layer properties
Tie layers are not only crucial for adhesion but also influence the integrity of the moisture barrier. High-quality tie layers prevent delamination under stress or high humidity conditions, maintaining the continuous barrier structure that protects the product. Choosing tie layers compatible with both core barrier and outer layers enhances performance under various storage conditions.
Surface treatments and coatings
Beyond material selection and layer design, surface treatments and coatings play an essential role in moisture barrier performance.
- Metalized coatings: Applying a thin metal layer, such as aluminum, significantly reduces moisture transmission. While metalized films are effective, they can impact recyclability and transparency.
- Silicone oxide or aluminum oxide coatings: These inorganic coatings provide a uniform moisture barrier and are compatible with flexible packaging.
- Hydrophobic polymer coatings: Adding a hydrophobic layer on the exterior can repel moisture and improve barrier performance in humid environments.
These coatings are often combined with traditional multi-layer co-extrusion to maximize both barrier performance and film functionality.
Processing and extrusion considerations
The co-extrusion process itself influences the moisture barrier properties of the film. Key factors include:
- Temperature control: Precise extrusion temperatures ensure proper polymer flow and adhesion between layers. Poor temperature control can cause voids or weak interfaces, reducing moisture resistance.
- Layer uniformity: Even, consistent layers prevent localized weak points where moisture could penetrate.
- Cooling rate: Proper cooling stabilizes the film and prevents shrinkage or warping, maintaining layer integrity.
Manufacturers must invest in advanced co-extrusion equipment and quality control to achieve multi-layer co-extruded barrier film with optimal moisture resistance.
Heat sealing and film finishing
The inner seal layer not only enables packaging but also contributes to moisture barrier performance. Films with strong, uniform seals prevent water vapor ingress at seams and edges. Some strategies to enhance sealing performance include:
- Optimizing sealant polymer composition
- Adjusting sealing temperature and dwell time
- Using laminated structures where the seal layer is protected by an outer barrier
Additionally, film finishing techniques such as surface smoothing and antistatic treatments reduce micro-cracks and surface irregularities that could compromise moisture protection.
Testing and quality assurance
Ensuring that multi-layer co-extruded barrier film meets moisture barrier requirements requires rigorous testing. Common evaluations include:
- Water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) testing: Measures the amount of moisture that passes through the film under controlled conditions.
- Humidity cycling tests: Simulate real-world storage conditions to assess barrier integrity over time.
- Seal strength tests: Confirm that heat seals maintain a moisture-tight closure.
High-quality films must consistently pass these tests to provide reliable moisture barrier performance.
Applications driving moisture barrier improvements
Several industries rely on multi-layer co-extruded barrier film with enhanced moisture resistance:
- Food packaging: Protects dry, frozen, and perishable goods from moisture-induced spoilage.
- Pharmaceutical packaging: Maintains product stability, particularly for moisture-sensitive medicines and powders.
- Industrial products: Preserves chemicals, electronic components, and other moisture-sensitive items.
In these applications, enhanced moisture barrier performance translates to longer shelf life, reduced waste, and improved product quality.
Sustainability considerations
As environmental concerns grow, multi-layer co-extruded barrier film must balance performance with sustainability. Key approaches include:
- Using recyclable polymer combinations: Reducing the number of incompatible layers simplifies recycling.
- Incorporating recycled content: Ensures environmental benefits without compromising moisture barrier properties.
- Reducing thickness without performance loss: Advanced co-extrusion and barrier materials allow thinner films with equivalent moisture resistance, reducing material usage.
Sustainable strategies are increasingly important for buyers seeking eco-friendly packaging solutions without sacrificing functionality.
Market trends and buyer considerations
Buyers of multi-layer co-extruded barrier film are increasingly focused on performance, cost, and environmental impact. Key considerations include:
- Performance customization: Selecting films with barrier levels appropriate for specific products.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensuring films meet food safety, pharmaceutical, or industrial standards.
- Supplier reliability: Partnering with manufacturers that maintain strict quality control.
- Innovation adoption: Leveraging advanced polymers, coatings, and extrusion techniques to achieve superior moisture resistance.
These factors influence purchasing decisions and drive demand for high-performance multi-layer co-extruded barrier film.
Improving moisture barrier performance in multi-layer co-extruded barrier film requires a combination of material selection, layer optimization, advanced extrusion techniques, surface treatments, and quality assurance. Manufacturers can tailor films to meet the specific requirements of food, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications while balancing performance, cost, and sustainability.


 English
English عربى
عربى